By Huiwen Biology & Iwase Cosfa Korea
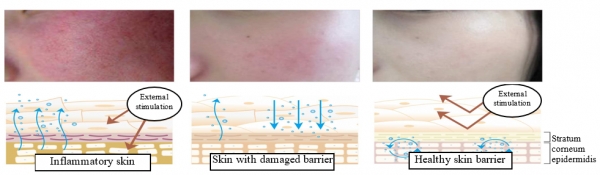
In current society, it has become a behavioral habit that consumers are paying more and more attention to personal protection, and wearing masks for outdoor activities. In fact, skin, the largest physiologic barrier of human body, plays an important protective role in preventing the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms from the outside world and controlling the substances to run in or out of human body. Owing to the functional integrity of skin barrier, healthy skin can resist the external simulation and the invasion of pathogenic microorganisms so that it has no allergic reaction and inflammatory symptoms and stays hydrated and healthy.
However, under the pressure of modern living environment, skin is constantly stimulated by external environment, e.g. physical stimulation (alcohol, disinfectant, etc.), pathogenic microorganism stimulation, oxidative pressure stimulation, and so on. Once such stimulation exceeds the rate and intensity of skin restoration, skin barrier will be continuously damaged. Later, skin barrier will be broken, and thus skin releases inflammatory factors and begins to suffer inflammatory injury, which will further destroy skin barrier. Finally, skin will get caught with incomplete barrier, low tolerance, reddening & itching, dryness and other discomfort symptoms.
There are three commonly-used ways for cosmetics to enhance skin barrier: adding moisturizing agent(s), adding film-forming agent(s), and adding active substance(s) that can activate the structural barrier. Commonly-used moisturizing agents, e.g. glycerin, containing natural moisturizing factors, have an instant moisturizing effect, but their lasting moisturizing effect is insufficient. Film-forming agents have a function of sealing and shielding, but the films formed are inelastic and crackly, which will affect the moisturizing effect. Active substances that can activate the structural barrier generally have a single function and are slow to take effect.
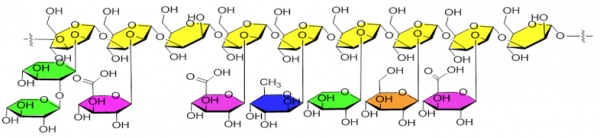
WSK is a natural macromolecular phyto-polysaccharide, extracted from Tremella fuciformis, formed by repeated structural moiety: the main chain composed of 9 mannoses in left helix mannan , as well as the branch chains composed of xylose, fucose, glucuronic acid and glucose . Its molecular weight is more than 3 million dal. Owing to the unique main chain + side chains structure, the polysaccharide can form stable hydrogen bonds with water molecules, to lock up a large amount of water. At the same time, a large amount of hydroxyl groups in the polysaccharide also can form stable hydrogen bonds with each other after losing free water molecules, and then form macromolecular polymers with cross-linked hydrogen bonds. Therefore, the polysaccharide has excellent moisturizing and film-forming abilities. Mannan is the main capsular polysaccharide of living organisms. After binding mannan with human immune cells, it will generally cause a series of immunological reaction (different types of mannan can respectively cause inhibition or activation of immunity) so as to regulate human immunity. WSK is a manna heteropolysaccharide extracted from tremella fuciformis. According to the long-term research made by Huiwen Biology, when human immunity behavior too low, it can enhance the immunity; when human immunity is too high, it can suppress the immunity. Its structural characteristics and experimental studies have shown that it can enhance skin barrier, inhibit inflammatory factors, and improve dry, sensitive and damaged skin.
I. WSK enhances skin barrier
1.1 Moisturizing ability of WSK
The natural structure of WSK determines that it contains a large amount of hydroxyl groups and carboxyl groups. A spatial network structure is formed by swelling of these groups in solution, and can lock water molecules firmly, showing that WSK has a super-strong moisturizing ability.
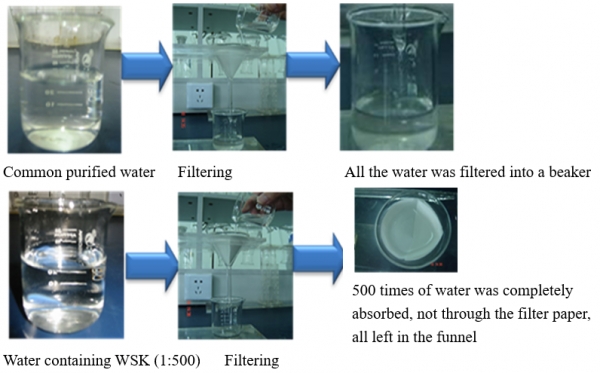
After WSK absorbs 500 times of its own water, carbohydrate chains will be opened and then form a huge complex spatial network structure. The intermolecular hydrogen-bond network structure formed by carbohydrate chains has an excellent water binding ability. After applying WSK on the skin, it can deliver its own moisture to skin, help skin to replenish more moisture quickly, instantly improve the moisture content of stratum corneum, and finally achieve an effect of skin moisturizing and dry skin improvement.
1.2 Film-forming ability of WSK
In structure, WSK forms a 3D network structure with xylose, fucose, glucuronic acid and glucose as the branch chains and with mannose as the main chain, with a good film forming ability. The film formed has high elasticity and softness.

WSK film is softer and more elastic than sodium hyaluronate film. After applying WSK on skin, it will bring a smooth and moist skin feeling, and the phenomenon of mud rubbing will not appear.
1.3 WSK promotes the relative expression of tight junction proteins
One of the most important ways to enhance skin barrier is to promote the expression of structural proteins in epidermal cells. Among them, the banded proteins wrapping the periphery of keratinocytes, namely tight junction proteins, play an important role in fixing keratinocytes, preventing the penetration of substances between cells and improving the barrier function.
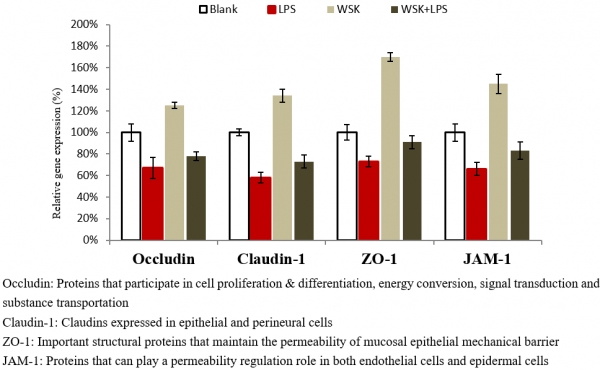
As shown in Fig. 6, after comparison between 0.1% WSK and 10ppm LPS, the relative gene expression of tight junction proteins (Occludin, Claudin-1, ZO-1, JAM-1) were significantly improved, indicating 0.1% WSK significantly promoted skin barrier enhancement. Moreover, protein expression for simultaneously adding 0.1% WSK and 10ppm LPS was higher than that for only adding 10ppm LPS, indicating that 0.1 WSK had a certain restoration effect on barrier cell damage caused by 10ppm LPS. Therefore, WSK has a skin barrier enhancement and restoration function.
II. WSK inhibits the inflammatory factors produced by external stimulation
2.1 WSK inhibits the inflammatory factors produced by lactic acid stimulation
WSK not only can enhance and restore skin barrier, but also can resist the stimulation of external lactic acid, thus reducing the production of inflammatory factors and slow down the inflammatory injury to skin barrier.
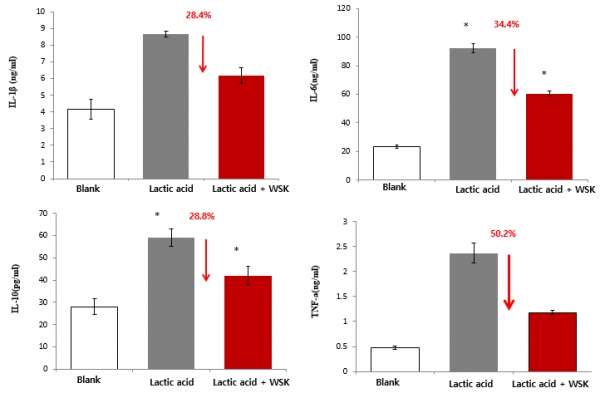
As shown in Fig. 7, compared with adding 0.3% lactic acid, adding 0.3% lactic acid and 0.1% WSK could inhibit the expression of the inflammatory factors ILs (IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-10) and the tumor necrosis factor TNF-a in the 3D skin model, and respectively reduced the expression by 28.4%, 34.4%, 28.8% and 50.2%. This indicates WSK can help skin barrier resist the simulation of fruit acids in cosmetics and reduce a variety of inflammatory factors produced by acid stimulation so as to restore the health of skin barrier.
2.2 WSK inhibits the inflammatory factors produced by 1,2-hexanediol
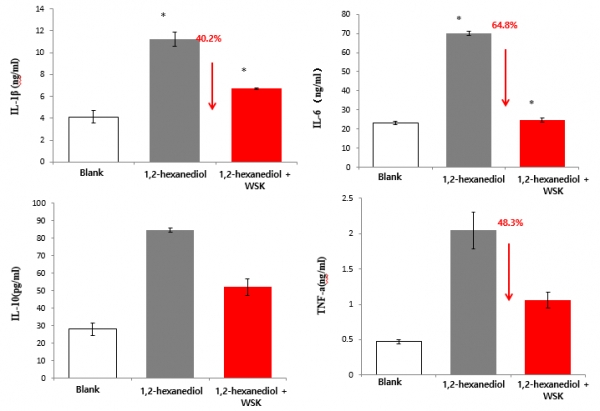
As shown in Fig. 8, compared with adding 0.3% 1,2-hexanediol, adding 0.3% 1,2-hexanediol and 0.1% WSK could significantly reduce the expression of the inflammatory factors ILs (IL-1 β, IL-6, IL-10) and the tumor necrosis factor TNF-a in the 3D skin model, and respectively reduced the expression by 40.2%, 64.8%, 38.5% and 48.3%. This indicates WSK can help skin barrier resist the simulation of diol preservatives in cosmetics and reduce a variety of inflammatory factors produced by diol simulation so as to restore and enhance the health of skin barrier.
III. WSK improves the damaged skin of human body
WSK can enhance skin barrier function, resist external stimulation, and inhibit a variety of inflammatory factors produced by external stimulation, so it has a significant improvement effect on the damaged skin such as saccharified skin and dry skin.
3.1 WSK inhibits the carbonylation of stratum corneum proteins
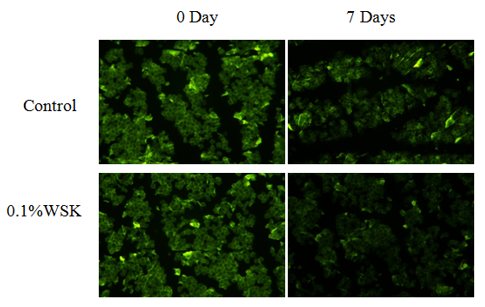
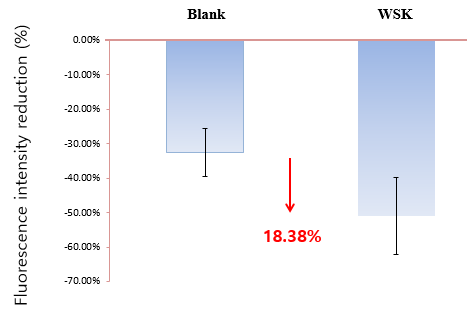
As shown in Fig. 9 and Fig. 10, after respectively applying a blank sample and a sample containing 0.1% WSK on the volunteers’ arms and taking images by fluorescence microscope, it is found through Image J fluorescence analysis that stratum corneum fluorescence intensity 7 days after applying 0.1% WSK was significantly weaker than that 0 day after applying 0.1% WSK, and fluorescence intensity was reduced by 18.38%. This indicates that WSK has a significant inhibitory effect on protein carbonylation of stratum corneum, and can enhance the adhesion of keratinocytes, better protect the skin barrier function, and improve the skin smoothness and integrity.
3.2 WSK reduces the trans-epidermal water loss (TEWL) of damaged skin and increases the water content of stratum corneum (WCSC)
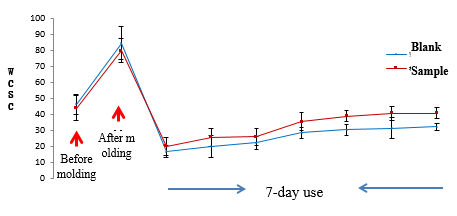
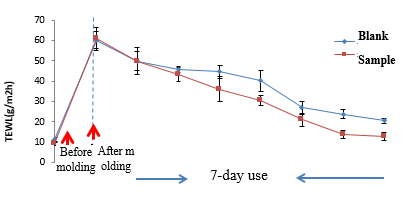
As shown in Fig. 11 and Fig. 12, after treating the forearm skin of volunteers with 1% SDS solution for 24h, applying blank sample and 0.1% WSK sample on the positions with a decrease in the skin barrier thickness, and testing the positions with CK TEWL and WCSC probes every day, it is found that WCSC of volunteers treated with SDS decreased to the same level and their TEWL increased to the same level. Within 7 days after application, on each day from the first day to the last day, WCSC of volunteers in the experimental group was higher than that in the blank group, and TEWK of volunteers in the experimental group was lower than that in the blank group. This indicates that WSK can protect the damaged skin to maintain high moisture, fight against dry skin, and achieve a lasting moisturizing effect.
3.3 WSK improves the damaged skin that is dry
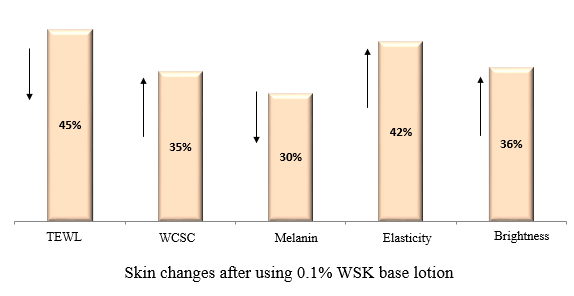
As shown in Fig. 13, ten volunteers were selected from Shanghai, among which there were 6 females and 4 males, aged from 22 to 40 years old, with skin barrier damage as determined by doctors. The volunteers continuously used 0.1% WSK base lotion respectively in the morning and evening (two times per day) for 30 days. Respectively 0, 15 and 30 day(s) after that, CK multi-probe was used to test their skin to collect face data, and VISIA was used to collect face images. Based on comparison of the situation after using 0.1% WSK base lotion for 30 days and that before use, it was found that TEWL decreased by 45% and WCSC increased by 35%. This indicates that WSK can help skin restore and enhance its barrier. In addition, melanin decreased by 30%, and skin elasticity and brightness respectively increased by 42% and 36%. This indicates that WSK can resist external stimulation and inhibit the production of melanin after the damaged skin barrier is restored to integrity and WSK is more conducive to make skin hydrated and healthy and improve skin flexibility and brightness after the skin moisture retention is improved.
3.4 WSK improves the damaged skin that is reddish
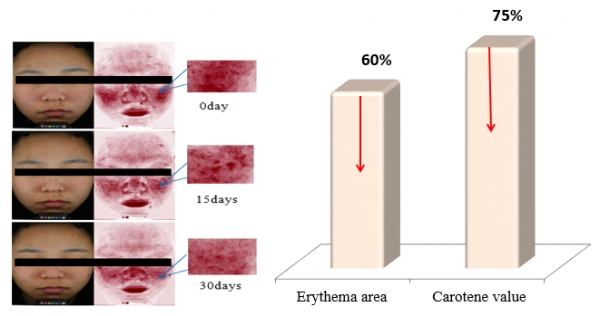
As shown in Fig. 14, ten volunteers were selected from Shanghai, among which there were 6 females and 4 males, aged from 22 to 40 years old, with skin barrier damage as determined by doctors. The volunteers continuously used 0.1% WSK base lotion respectively in the morning and evening (two times per day) for 30 days. Respectively 0, 15 and 30 day(s) after that, CK multi-probe was used to test their skin to collect face data, and VISIA was used to collect face images. Based on comparison of the situation after using 0.1% WSK base lotion for 30 days and that before use, it was found that erythema area decreased by 60% and carotene value decreased by 75%. This indicates that WSK has a significant inhibitory effect on skin redness caused by skin damage, and might also reduce the release of inflammatory factors and slow down the inflammatory reaction. WSK can better improve skin sensitivity and redness caused by skin dryness and fragility.
IV. Conclusion
WSK, as a naturally derived heteropolysaccharide, can enhance skin barrier through moisturizing, film-forming and simultaneous promotion of three-level expression of tight junction proteins so as to play a role in resisting external stimulation and injury, inhibiting the expression of inflammatory factors as well as protecting and restoring skin barrier. WSK can be used in creams, lotions, masks, essences, hand creams or body creams that can enhance skin barrier, increase moisturizing ability, and improve sensitive skin and damaged skin.
Contacts
Iwase Cosfa Korea Co., Ltd.
Director. Lee Kyoungmin
Telephone. +82-10-9010-4951
E-mail. kmlee@cosfa.co.kr