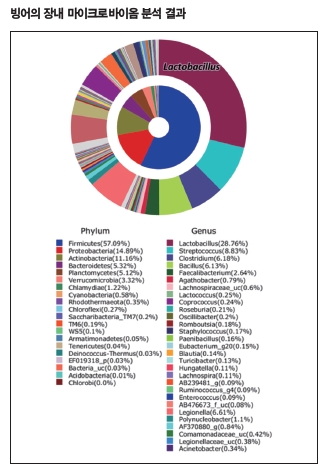
Nakdonggang National Institute of Biological Resources of the Ministry of Environment analyzed the intestinal microbiome of 11 species of fish including smelt, a representative fish species in winter, and found that Lactobacillus, which is the most commonly used as probiotics, exists at a high ratio inside the smelt's intestine.
Of 19 probiotics (defined as bacterial microorganisms that can be beneficial to the health of the host if administered in an appropriate amount, World Health Organization) desiginated by The Minstry of Food and Drug Safety's Notice (standard of health-functioning foods), 11 are Lactobacillus. The analysis of the intestinal microbiome of the smelt showed that the proportion of lactobacillus within a colony averaged 28.8% (15.3-55.5%), significantly higher than the rate found in the intestines of other living organisms (0.01% in humans and not detected in 10 other fish species). In addition, lactic acid bacteria such as Bifidobacterium (average 5.3%) were also found to be the major taxa.
Lactobacillus is reported to be 236 species worldwide as of 2018, and it has been studied in the dairy industry as a typical bacteria used for fermented food such as kimchi and cheese. Recently, intestinal microbiome research has become active, and the health promotion effect of Lactobacillus and its potential for utilization have attracted much attention. Especially, this smelt research is the first result showing that the L. helveticus group is the dominant group among the Lactobacillus.
The discovery of this intestinal microbiome of smelt, which could be distinguished from the results of microbiome studies of other 10 species of fish dominated by Bacteroidetes and Proteobacteria, is expected to lead to a scientific approach to the use of smelt in future.